 |
|
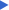
Range of Acer negundo
from "Atlas of United States Trees"
- Elbert L. Little, Jr.
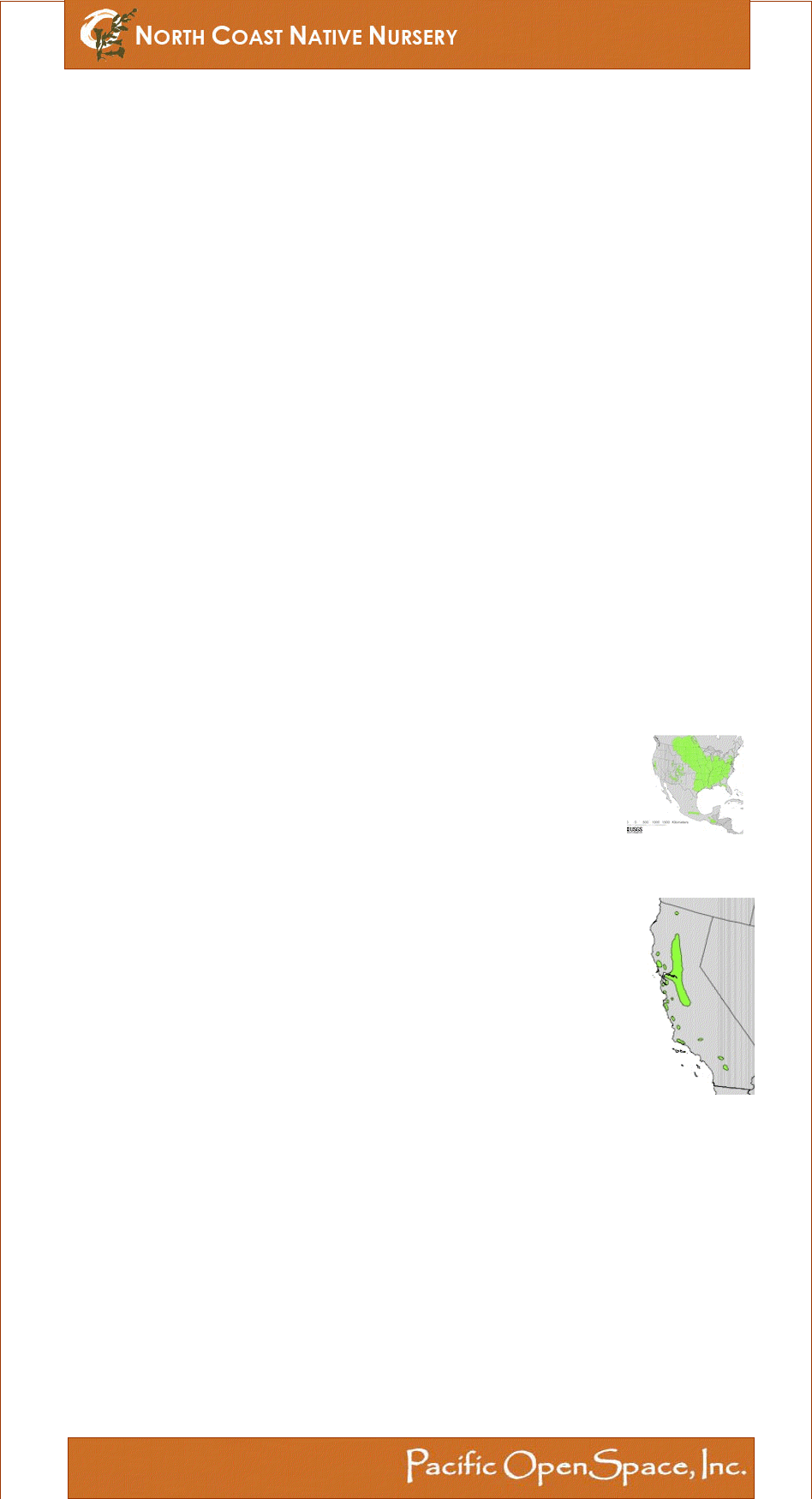
Range of Acer negundo var.californicum
from "Atlas of United States Trees"
- Elbert L. Little, Jr.
Box Elder
Acer negundo var. californicum
Cronquist System |
|
Order: |
Sapindales |
Family: |
|
Genus: |
|
APG System |
|
Order: |
Sapindales |
Family: |
Sapindaceae |
Genus: |
|
Description |
|||
Description: |
Acer negundo is a deciduous tree with a rounded crown. It grows as hig as 60 ft. , but 30 to 40 feet is more typical for an open grown tree, and 15 to 20 feet for one in the shade. |
||
Branching: |
Opposite |
||
Leaves: |
Pinnately compound leaves. There may be as few as three leaflets, but five or seven leaflets per leaf is more common. |
||
Flowers: |
Box elder flowers grow in panicles or racemes. They are pink in color. Flowering is often in March or April, sometimes as late as May. |
||
Fruit: |
The seeds are in doubles, hanging by a stem from the branch. Each seed has a wing. |
||
Plant Relationships |
|||
Related California Species: |
Acer circinatum |
Vine maple |
|
Related Exotic Species: |
Acer rubrum |
Red maple |
|
Growing Conditions |
|||
Natural Range and Habitat: |
Acer negundo is found throughout the United States and much of Canada, from coast to coast. It is more common east of the Missouri and east of the Mississippi. The local variety, Acer negundo var. californicum, is endemic to California. |
||
Sun and Exposure: |
Box elder is shade tolerant, and is commonly found in riparian woodlands, however, shade grown plants have poor form, and have small, weak branches. The plant requires full sun to achieve a good form. |
||
Soil and Moisture Requirements: |
Acer negundo grows where there is a stable water source during the summer. This can be a riparian zone, an elevated water table or a spring. |
||
Horticulture and Restoration |
|||
Wildlife Habitat: |
|||
Restoration: |
Acer negundo var. californicum is most commonly used in riparian restoration projects, often in the shade. |
||
Uses in Landscaping: |
When grown in the full sun in good conditions, it has the typical, sturdy maple tree appearance and can grow fairly large. If grown in the shade, as in a riparian zone, it is much reduced in size, with many small branches. |
||
Horticultural Comments: |
Sunset zones 1-10 and 12-24. |
||
Back to start page